
New research has found motorists generate over 107,000 tonnes of CO2 annually in the UK, just by idling to warm up their cars in winter months.
That's more than if the whole population of Cardiff caught a flight to Egypt for COP27.
It squanders a combined £188 million on fuel costs… and does no good for the environment, their finances or even their cars.
The study, which was published last week by the Institution of Engineering & Technology (IET), found that six in ten (64%) drivers let their engine idle during the colder months, with 41% doing so at least three times a week.
More than a million motorists idle every single day during winter (an estimated 244 minutes), producing a carbon footprint over a lifetime of 825kg.
Highlighting the extent of the issue, the average idle time during winter is 4.79 minutes but one in six (15%) motorists leave their car running for at least 10 minutes - to get everything – including the interior – warm.
The research, undertaken ahead of COP27, highlights the whole-scale change required to meet the government’s 2030 net zero goals.
Although electric vehicles have been attributed as the solution to reducing emissions, two-thirds (66%) of motorists said it was highly unlikely they will be driving one before the government’s ban on the sale of new petrol and diesel cars comes into effect in 2030.
Over half of motorists (55%) who were planning to buy an EV in the next two years, are now delaying doing so because of concerns about their finances – a decision that could accumulate 327,500 tonnes of CO2 every year.
Seven in ten (71%) of the drivers questioned said they were more likely to make the switch to electric if government grants were reinstated and 67% said they would buy an EV as their next car if money wasn’t a factor.
Proving it’s not just the planet that’s worse off, motorists with a petrol or diesel vehicle are squandering a combined £188 million on fuel costs whilst idling over winter – enough to pay for more than 75,000 homes to be heated for the whole year.
This holds a sense of irony as one of the biggest challenges is the common misconception that motorists need to warm up their car on a cold day.
An overwhelming 65% of the drivers questioned had heard this anecdote with four in ten (42%) believing it helps extend the lifespan of the car engine itself.
Commenting on this issue, Farooq Yaqub, Member of the IET’s Council and EV expert, said:
“If you use your car every day, then there is no need to warm up the car engine – an idling engine can produce up to twice the emissions of a car in motion.
“Excessive idling can also actually damage your engine’s components, including spark plugs, cylinders and exhaust systems.
“The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) will be so critical in the long-term in helping reduce emissions from petrol and diesel engines.
“Yet the research has demonstrated a clear financial barrier to this being a straightforward process, amplified by the cost-of-living crisis.
“This is why it’s so important that the government provides further support and incentives for EV uptake if they are serious about meeting their 2030 net zero goals.”
To help Britons save money and the planet in the meantime, the IET has developed some top tips to help lower motorists’ winter idling carbon footprint.
- De-ice your windscreen – You can remove frost or snow without having to warm up your engine by using an ice scraper and de-icer.
- Myth busting – You do not need to warm up the engine before driving in your car. The operating temperature is quickly reached, and the emissions management devices are active in the meantime.
- Park inside – If possible, park your vehicle inside, such as in a garage, to avoid frost build-up and to ensure a more comfortable temperature when you first get in.
- 10 second rule – If you're going to be stationary for more than 10 seconds, it's best to turn off your engine; restarting does not increase fuel consumption. Alternatively, if your vehicle has a start/stop feature, make sure it is turned on.
- Route optimisation – Use real-time navigation apps to help you avoid traffic and thus spend less time idling. Occasionally driving slightly longer distances at more consistent speeds will not only get you to your destination faster, but will also help the engine run more efficiently.
- Right tool for the job – Diesel and gasoline vehicles have distinct characteristics, and using them for appropriate applications is critical to achieving higher efficiency and lower emissions. i.e., Diesel vehicles are more suited for motorway journeys.
To find out more about your winter idling carbon footprint and electric vehicles, visit IET’s Instagram, Facebook, Twitter or LinkedIn.
 Man Charged After Throwing Brick Through Brighton Restaurant Window
Man Charged After Throwing Brick Through Brighton Restaurant Window
 Peacehaven Man Disqualified Over High-Speed A27 Pursuit Near Brighton
Peacehaven Man Disqualified Over High-Speed A27 Pursuit Near Brighton
 Appeal After PCSO Assaulted In Uckfield
Appeal After PCSO Assaulted In Uckfield
 Man Charged With Rape Of Teenage Girl In Newhaven
Man Charged With Rape Of Teenage Girl In Newhaven
 Overnight Closures For A22 Forest Row Road Improvements
Overnight Closures For A22 Forest Row Road Improvements
 Brighton Defence Manufacturer's Controversial Planning Application Likely To Be Heard
Brighton Defence Manufacturer's Controversial Planning Application Likely To Be Heard
 Over £2.4m Approved For Worthing School Support Centre
Over £2.4m Approved For Worthing School Support Centre
 Section Of M25 To Close Again Tonight - As Drivers Warned Not To Get Complacent
Section Of M25 To Close Again Tonight - As Drivers Warned Not To Get Complacent
 Plans For 800 New Horsham Homes Refused
Plans For 800 New Horsham Homes Refused
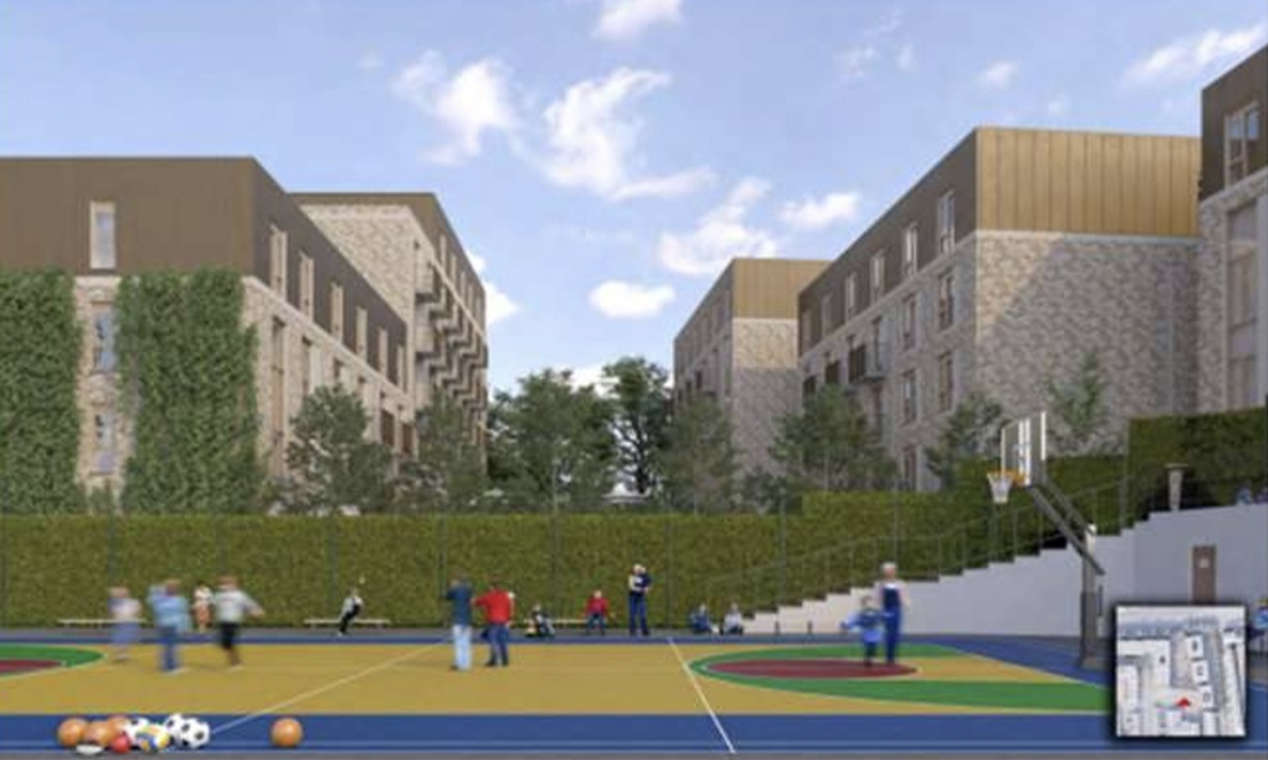 Over 200 Co-Living Flats Approved For Brighton
Over 200 Co-Living Flats Approved For Brighton